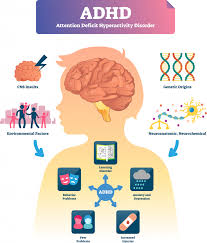
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a common neurodevelopmental disorder affecting both children and adults. Characterized by symptoms such as inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsiveness, ADHD disorder can pose significant challenges in daily life. However, with the right strategies and support, individuals with ADHD can lead successful and fulfilling lives. This article delves into supportive strategies and practical tips to manage ADHD disorder effectively.
Understanding ADHD Disorder
ADHD disorder manifests in three primary types: predominantly inattentive presentation, predominantly hyperactive-impulsive presentation, and combined presentation. Understanding the specific type and its characteristics is crucial for tailoring appropriate coping strategies.
Creating a Supportive Environment
At Home
A structured and organized home environment can significantly aid individuals with ADHD. Clear routines and designated activity spaces help reduce distractions and promote focus.
-
Establish Routines: Consistent daily schedules provide predictability and reduce the mental load of decision-making. Set regular times for waking up, meals, homework, and bedtime.
-
Declutter Spaces: A tidy, organized space minimizes distractions. Use storage solutions to keep items in their designated places.
-
Visual Aids: Calendars, charts, and checklists can be helpful tools for keeping track of tasks and responsibilities. Visual reminders help manage time and stay on track.
At School
For children with ADHD, a supportive school environment is essential. Collaboration between parents, teachers, and school counselors can lead to effective strategies tailored to the child’s needs.
-
Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): These plans provide tailored educational accommodations, such as extended time on tests or modified assignments.
-
Breaks and Movement: Regular breaks and opportunities for physical movement can help children with ADHD release energy and maintain focus.
-
Positive Reinforcement: Encouragement and positive feedback reinforce good behavior and academic efforts, boosting self-esteem and motivation.
Behavioral Strategies
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT is an effective treatment for managing ADHD symptoms. It helps individuals develop coping skills, challenge negative thoughts, and improve emotional regulation.
-
Goal Setting: CBT encourages setting realistic and achievable goals, breaking them into smaller steps to foster a sense of accomplishment.
-
Self-Monitoring: Keeping a journal or using apps to track behavior patterns and triggers can provide insights and help develop coping mechanisms.
Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques
Mindfulness practices and relaxation techniques can improve concentration and reduce impulsivity.
-
Meditation: Regular mindfulness meditation can enhance attention and reduce stress.
-
Breathing Exercises: Simple breathing exercises help calm the mind and improve focus, especially during stressful situations.
Medication and Medical Interventions
Medication can be a critical component of ADHD treatment for many individuals. Working closely with healthcare providers to find the proper medication and dosage is essential.
-
Stimulant Medications: Commonly prescribed medications like Adderall and Ritalin help increase focus and reduce impulsive behavior.
-
Non-Stimulant Medications: For some, non-stimulant medications such as Strattera may be more effective or preferred due to fewer side effects.
-
Regular Monitoring: Regular follow-ups with healthcare providers ensure the effectiveness of the medication and allow for adjustments as needed.
Practical Tips for Daily Management
Time Management
Effective time management strategies can help individuals with ADHD stay organized and productive.
-
Use Timers and Alarms: Setting alarms for tasks and deadlines helps manage time effectively and stay on schedule.
-
Prioritize Tasks: Break tasks into smaller, manageable steps and prioritize them based on importance and deadlines.
-
Avoid Multitasking: Focus on one task at a time to ensure better quality work and completion.
Organization and Planning
Organizational skills are crucial for managing the chaos often associated with ADHD.
-
To-Do Lists: Creating daily to-do lists helps track tasks and reduces the likelihood of forgetting essential activities.
-
Digital Tools: Utilize digital tools and apps for reminders, calendar events, and task management.
-
Simplify Tasks: Simplify complex tasks into smaller, more manageable components.
Seeking Support and Building a Network
Support Groups
Connecting with others who understand the challenges of ADHD disorder can provide emotional support and practical advice.
-
Local and Online Groups: Join support groups in your community or online to share experiences and strategies.
-
Family and Friends: Educate family and friends about ADHD to build a supportive network that understands and accommodates your needs.
Professional Help
Professional support from therapists, coaches, and counselors can provide personalized strategies and interventions.
-
ADHD Coaches: ADHD coaches specialize in helping individuals develop skills and strategies to manage their symptoms effectively.
-
Therapists and Counselors: Regular therapy sessions can help in addressing the emotional and psychological challenges associated with ADHD.
Conclusion
Coping with ADHD disorder involves a combination of strategies tailored to individual needs. By creating supportive environments, employing behavioral strategies, managing time effectively, and seeking professional help, individuals with ADHD can thrive. Embracing a multifaceted approach ensures that the unique challenges of ADHD are met with practical and effective solutions, leading to improved quality of life and overall well-being.